All about Roar Solutions
All about Roar Solutions
Blog Article
An Unbiased View of Roar Solutions
Table of ContentsThe 7-Minute Rule for Roar SolutionsEverything about Roar SolutionsOur Roar Solutions Statements
In order to protect installments from a potential surge an approach of analysing and identifying a potentially unsafe area is needed. The function of this is to guarantee the appropriate option and setup of tools to eventually protect against an explosion and to ensure safety of life.
(https://my.omsystem.com/members/roarsolutions)
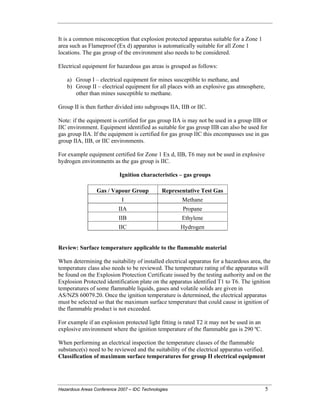
No devices needs to be mounted where the surface temperature of the equipment is more than the ignition temperature of the provided danger. Below are some usual dirt hazardous and their minimum ignition temperature. Coal Dust 380C 225C Polythene 420C (thaws) Methyl Cellulose 420C 320C Starch 460C 435C Flour 490C 340C Sugar 490C 460C Grain Dust 510C 300C Phenolic Resin 530C > 450C Aluminium 590C > 450C PVC 700C > 450C Soot 810C 570C The likelihood of the risk existing in a concentration high enough to trigger an ignition will differ from area to place.
In order to identify this threat a setup is split into locations of threat depending upon the amount of time the dangerous exists. These areas are described as Areas. For gases and vapours and dusts and fibers there are 3 zones. Zone 0 Area 20 A hazardous ambience is very most likely to be present and might exist for lengthy periods of time (> 1000 hours per year) or perhaps continually Zone 1 Zone 21 A hazardous environment is feasible yet not likely to be present for long periods of time (> 10 450 C [842 F] A category of T6 implies the minimum ignition temperature is > 85 C [185 F] Hazardous location electric equipment possibly created for usage in higher ambient temperature levels. This would certainly suggested on the rating plate e.g. EExe II C T3 Ta + 60C( This suggests at 60C ambient T3 will certainly not be exceeded) T1 T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6 T2 T2, T3, T4, T5, T6 T3 T3, T4, T5, T6 T4 T4, T5, T6 T5 T5, T6 T6 T6 A T Course rating of T1 suggests the maximum surface area temperature produced by the instrument at 40 C is 450 C. Presuming the associated T Course and Temperature ranking for the devices are appropriate for the location, you can constantly use a tool with a more rigorous Division rating than required for the area. There isn't a clear answer to this inquiry unfortunately. It truly does depend upon the kind of tools and what fixings need to be lugged out. Equipment with certain test treatments that can't be done in the area in order to achieve/maintain 3rd party ranking. Need to return to the factory if it is prior to the devices's solution. Field Repair Service By Authorised Personnel: Complex screening might not be required nevertheless details treatments might need to be complied with in order for the tools to keep its third event rating. Authorized employees must be utilized to do the job correctly Repair work need to be a like for like replacement. New component have to be thought about as a direct replacement needing no special screening of the equipment after the repair is full. Each tool with a dangerous score need to be evaluated independently. These are detailed at a high degree listed below, however for even more thorough info, please refer straight to the standards.
The smart Trick of Roar Solutions That Nobody is Talking About
The devices register is an extensive database of equipment documents that includes a minimum collection of areas to determine each thing's location, technical specifications, Ex lover classification, age, and environmental data. The ratio of In-depth to Close assessments will be figured out by the Devices Danger, which is analyzed based on ignition risk (the possibility of a source of ignition versus the probability of a flammable atmosphere )and the unsafe location classification
( Zone 0Area 1, or 2). Carrying out a robust Risk-Based Examination( RBI )method is important for guaranteeing compliance and safety in taking care of Electrical Tools in Hazardous Locations( EEHA).
The Best Strategy To Use For Roar Solutions
In terms of explosive threat, a hazardous location is an atmosphere in which an explosive atmosphere exists (or may be anticipated to be present) in quantities that call for special safety measures for the construction, installment and use of equipment. electrical refresher course. In this post we discover the obstacles dealt with in the office, the risk control steps, and the called for proficiencies to function safely
It issues of contemporary life that we make, store or handle a variety of gases or liquids that are deemed combustible, and a series of dusts that are regarded combustible. These materials can, in certain problems, develop eruptive atmospheres and these can have significant and heartbreaking consequences. A lot of us are familiar with the fire triangle get rid of any type of among the three aspects and the fire can not take place, but what does this mean in the context of unsafe areas? When breaking this down right into its simplest terms it is essentially: a mix of a particular quantity of launch or leakage of a particular compound or product, blending with ambient oxygen, and the existence of a source of ignition.
In many circumstances, we can do little concerning the degrees of oxygen in the air, but we can have considerable influence on resources of ignition, for instance electric tools. Unsafe areas are documented on the dangerous area classification drawing and are determined on-site by the triangular "EX LOVER" indication. Below, among various other essential details, areas are divided into 3 types depending upon the hazard, the probability and duration that an eruptive atmosphere link will certainly exist; Area 0 or 20 is considered one of the most harmful and Zone 2 or 22 is deemed the least.
Report this page